It is stated that data fabric is a must-have element for all organizations that are data-centric. For the past few years, this terminology has been quite relevant with enterprise data management and enterprise data integrations. According to analyst firm Gartner, data fabric is considered to be the top 10 data and analytics trends for 2021. Gartner also estimates that by the year 2024, almost 25% of every data management vendor will be providing a comprehensive data fabric solution. This will be a huge jump from the current contribution of 5%.
What is data fabric?
To put it in simple terms, data fabric is a simplified, unified, and single architecture that encompasses an integrated set of technologies and services. This collection is created to deliver integrated and enriched data using the correct methodology, to the right data customer and at the correct time; addressing both operational as well as analytical work.
Data fabric comprises key data management technologies such as – data catalog, data governance, data integration, data pipelining, and data orchestration.
Why do you need data fabric?
A fundamental reason why organizations need data fabric is that it serves many alignment drivers that are business, technical, and organizational in nature.
Business Drivers
- For business drivers, data fabric helps in reducing time to access insights and helps in a faster process of informed decision making. This is done by pipelining data into data warehouses and data lakes, quickly.
- Data fabric also helps in providing a real-time 360-degree view of all aspects of a business entity such as customers, vendors, orders, delivery, product, etc.
Organizational Drivers
- Data fabric serves as a common language between data engineers and data consumers, thereby helping in improved collaboration among business teams and data teams.
- There are self-service data access capabilities that allow consumers to get the data that they need, and at any given point in time.
Data management drivers
- Management of data preparation helps data scientists and other IT resources to avoid undertaking any sort of repetitive tasks around data enrichment, transformation, and data cleansing.
- Through data fabric, one can gain access to any sort of enterprise-wide data using any method. This includes bulk data movement, data virtualization, and even APIs.
- Data fabric also streamlines and integrates the current data management tools used in the organization, and optimizes other redundant ones for improving cost-effectiveness.
The architecture of Data Fabric
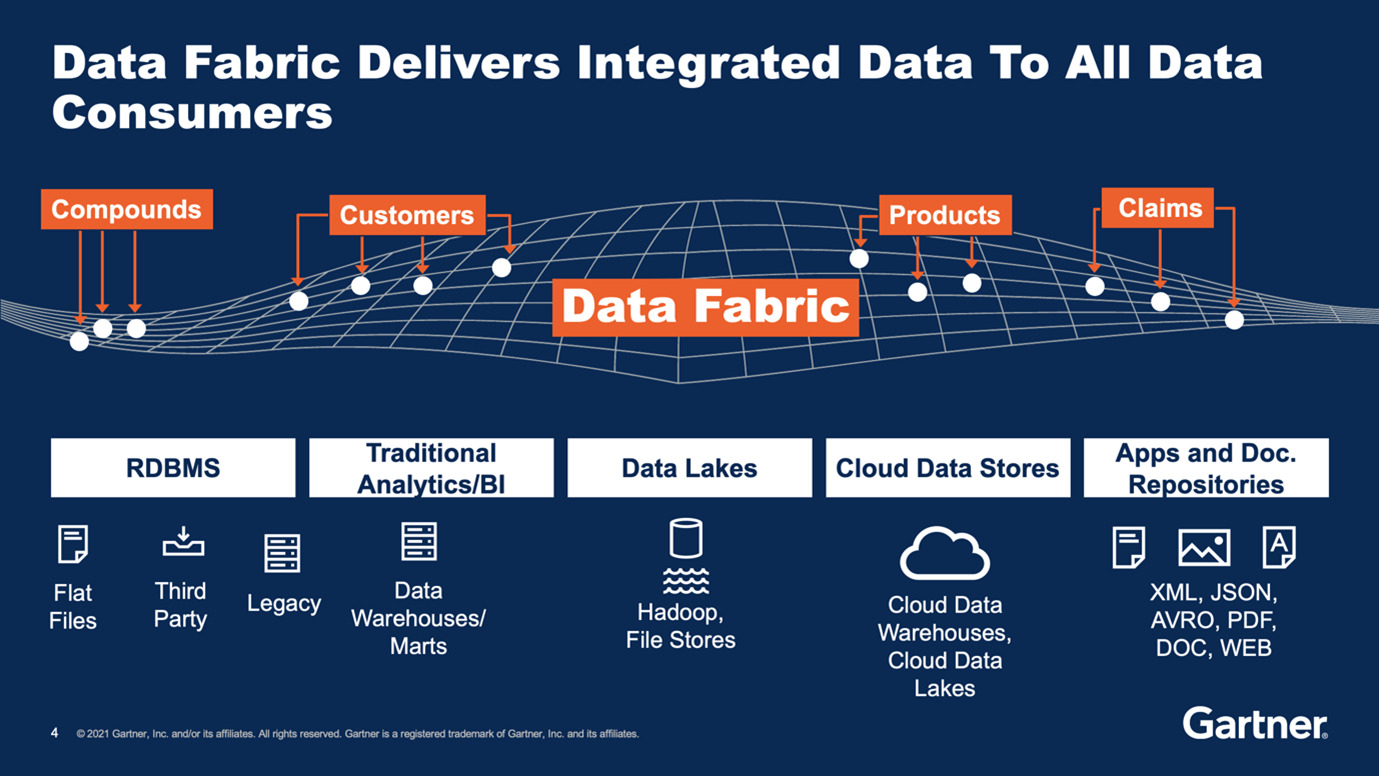
A data fabric architecture that is well defined is modular in nature and supports large-scale deployment that can be either multi-cloud, on-premise, or even a hybrid deployment. For a data fabric architecture, data sources range from many legacy systems that work in silos to the latest cloud environments.
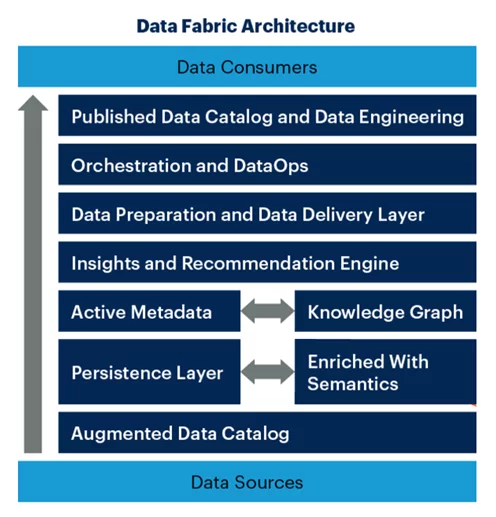
The following diagram gives an idea of the architecture of data fabric
Source: Gartner Inc., and/or its affiliates
Consumers of data fabric comprise data scientists and analysts, marketing analysts, sales analysts, and resources who work on data privacy along with cloud architects.
Key capabilities of data fabric
Following are the set of key capabilities that data fabric supports when it is integrated into a single unified platform:
- Data Catalog
To categorize, classify and put data assets into a proper inventory structure, thereby presenting it visually.
- Data Engineering
To develop reliable data pipelines for analytical and operational purposes
- Data Governance
To ensure the quality of data and also to comply with the regulations and protocols around data privacy, data safety, and scalability
- Data Preparation
This is about defining the process of data flow, which also includes steps involved in data cleansing, enrichment, transformation, and data validation.
- Data integration & data delivery
This involves extracting or retrieving data from any reliable source and then making it available for the data consumer for further processing. This is done through APIs, ETL, etc.
Over and above the core capabilities as mentioned above, there are certain non-core capabilities as well, which data fabric brings on to the table.
These are as follows:
- Scale, Volume & Performance of Data
- Accessibility
- Distribution
- Security
Comparison between Data Fabric/Data Lake/Database for Operational Workloads
To help you understand the significance of data fabric, let us look at a comparison around the pros and cons of various data sources
| Various data sources | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Data Lake, Data Warehouse | Support data queries across many structured and unstructured data |
Not really optimum for single entry data queries that cause slow responses. Does not support live data so continuous data updates are not reliable. |
| No SQL Database | Supports linear scalability through distributed datastore architecture | Does not support SQL so it requires specialized skills |
| Data Fabric | • Complete SQL support • Supports linear scalability through distributed datastore architecture • Supports high concurrency with real-time performance • Supports complex queries for single business entities • Supports all kinds of integration methodology • Flexible and dynamic data governance structure |
NA |
While data fabric does serve as a superior technology for high-scale operational workloads, it is also a solution that acts as a reciprocal technology to data lake and data warehouses. For such amount of data workloads, a data fabric can:
1. Pipeline fresh, trusted data INTO them, for offline analytics purposes.
2. Receive business insights FROM them, to embed into real-time operational use cases.
Use Cases of Data Fabric
Across enterprise operations, there are multiple used cases that require a high-scale and high-speed data architecture that is capable of supporting multiple transactions. These examples include:
-
Delivering a 360-degree customer view
Delivering a comprehensive and a single view of customers through CRM systems, IVR, or a customer self-service portal.
-
Adhering to data privacy laws
By adopting a flexible workflow and a data automation solution that complies with compliance between people, systems, and data.
-
Test data on demand
Helping in creating a test data warehouse and sharing anonymous test data to various data centers, maintaining total integrity
Advantages of Data Fabric
There are a plethora of advantages of data fabric over some of the traditional/alternative data management methodologies.
- Improved data management
- Expanded data services
- High level of consistency, availability, and durability
- Extremely tight security
- High performance
Final Thoughts
Teams that don’t want to have a single data fabric solution for data analytics and another solution for operational intelligence. They usually prefer to have a single data fabric for both.