Blockchain is a new technology that’s changing the way we handle transactions and store data. Simply put, it’s a shared digital ledger stored across a network of computers. Blockchain runs on three main principles:
- No one person or company controls it (decentralization).
- Everyone can see and check the transactions (transparency).
- Once something is added, it can’t be changed (immutability).
In finance, blockchain helps solve problems like high fees, slow payments, security risks, and fraud. The most well-known example is cryptocurrencies, which allow people to send money directly to each other without needing a bank.
Blockchain also makes international payments faster and cheaper. It’s used in finance for things like smart contracts, tokenization, and identity verification.
Smart Contracts: Automating Transactions
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms written directly into code. Once the term conditions are met, they automatically trigger an action, like releasing funds or transferring assets, without oversight from a third party.
Thus, they remove the need for middlemen like banks, lawyers, or brokers. This hastens the process, reduces transaction fees, and minimizes human error.
-
Financial Applications of Smart Contracts
Because of how they work, smart contracts have many financial applications:
- Loan Agreements: Smart contracts can manage payments, calculate interest, and update repayment schedules. They can also automatically release the next loan installment or adjust the contract status when payment terms are met.
- Insurance Claims: They can trigger claim approvals and payouts when the policyholder meets certain conditions, such as submitting required documents.
- Derivatives Trading: Smart contracts can execute complex trades instantly when the set market conditions are met.
- Purchasing and Selling: They can execute the sale of goods or assets after meeting predefined conditions, such as payment receipt or delivery confirmation.
Cross-Border Payments: Streamlining Transactions
Traditionally, international payments can often take days and involve multiple middlemen like banks and payment processors. These add up to the transaction costs and increase the risk of errors. Conversion fees can further complicate things, adding more expenses and inefficiencies.
Blockchain addresses these issues by cutting out intermediaries, which drastically reduces cross-border fees and processing times. Moreover, payments can be made in the recipient’s local currency, bypassing expensive conversion fees.
According to Deloitte, using blockchain can cut transaction costs by 40% to 80%. On top of that, these transactions typically take just four to six seconds to complete.
Fraud Prevention and Security: Enhancing Trust
Through encrypted and decentralized storage, organizations can store sensitive data in a more secure, tamper-proof way, staving off possible data breaches and identity theft. Moreover, since blockchain records every transaction publicly, hiding illegal activities like money laundering or fraud is more difficult.
These benefits rely on the following built-in security features:
- Cryptographic Hashing: This makes blockchain data hard to change. Each block is linked to the one before it through a unique code, or “hash,” so tampering with one block breaks the chain, making fraud easy to detect.
- Distributed ledger technology: Storing data across multiple nodes makes it difficult for hackers to compromise the system, as they would need to control the majority of nodes.
- Consensus Mechanisms: These include Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS). These mechanisms ensure all nodes agree on valid transactions, preventing double-spending and maintaining the integrity of the ledger.
- Pseudonymity: Cryptographic addresses allow users to transact without revealing their identities while still keeping transactions traceable.
A good example is J.P. Morgan’s usage of Liink, formerly known as the Interbank Information Network. It allows the secure exchange of payment-related information, reducing the risk of potential data theft.
( Also Read: Applications of Blockchain in Finance )
Tokenization of Assets: Democratizing Investments
Asset tokenization converts real-world assets into digital tokens on a blockchain. It breaks down high-value assets into smaller, more affordable pieces that anyone can own. This is known as fractional ownership.
The blockchain tracks ownership and makes sure the tokens can be safely traded, bought, or sold. This process opens investment to more people, making it less exclusive.
Platforms leading the way in asset tokenization include:
- RealT: Focuses on tokenizing real estate, giving investors the chance to own fractions of U.S. rental properties and earn income from dividends.
- Securitize: Specializes in tokenizing traditional financial assets, such as stocks and bonds, making them easier to trade on blockchain platforms.
1. Benefits of asset tokenization
- Accessibility: People from all walks of life can now invest, even in traditionally high-barrier markets like luxury real estate, stocks, or art.
- Increased liquidity: Tokens are more liquid, making it easier to buy or sell your portion whenever you want.
- Transparency: Since all token transactions are recorded on the blockchain, the process is more transparent, reducing the risk of manipulation.
Digital Identity Verification: Securing Financial Transactions
Fraud, identity theft, and inefficiency are common problems in traditional identity verification systems. Criminals can steal or fake personal data, and centralized databases (like those in banks) are vulnerable to hacking. The process also typically involves multiple steps and third parties, causing delays.
Blockchain addresses these issues through decentralization, making it harder for hackers to compromise data. It also gives users more control over what personal information they share. Blockchain records are immutable, so the data remains secure and reliable.
Payment Settlements: Increasing Speed and Efficiency
Depending on the country, settling trades typically takes T+2 days (trade date plus two days) or more. In the US, that’s T+1. Blockchain, with the help of smart contracts, can further reduce this to minutes or even seconds.
This allows investors to free up capital quickly, using their funds without waiting for long clearing processes. Additionally, blockchain provides a real-time view of transactions, reducing the risk of errors or disputes. A well-known platform for fast settlement using blockchain technology is Ethereum.
Benefits of Blockchain in Finance
1. Better Accuracy
Blockchain can record transactions with high accuracy. Since thousands of computers verify each transaction, the chances of human error are almost eliminated. Multiple computers must agree on a transaction’s validity before it’s added to the blockchain, ensuring only correct information is recorded.
2. Faster Transactions
Blockchain works 24/7, so transactions can be settled in minutes, regardless of time zones or weekends. This is especially useful for international payments, which generally take days to clear. Platforms like Ripple (XRP) allow cross-border payments to settle in a few seconds.
3. Better Security
Once a transaction is verified and added to the blockchain, it’s practically unchangeable. As mentioned, each block in the chain has its own unique code and is linked to the previous block. If you want to alter one block, you’d have to change all the blocks after it.
4. More Transparency
Most blockchain systems are open-source, meaning anyone can review the code. This allows for total transparency, as anyone can audit the system and see how it works. No single person or company controls public blockchains, making them trustworthy and open to updates if the majority agree.
5. Lower Costs
Blockchain removes the need for banks or notaries, reducing fees. When a business accepts credit card payments, they typically pay high processing fees. Blockchain transactions skip the banks and usually come with lower fees, saving both businesses and customers money.
6. Financial Inclusion
According to the World Bank, about 1.4 billion adults globally don’t have bank accounts. Blockchain and cryptocurrencies open up financial services to these people by just using the internet.
A good example of this is GiveDirectly. They use the Celo blockchain to deliver cash transfers directly to impoverished families in West Africa. People receive the money digitally and can use it to meet their daily needs without having to open a bank account.
Challenges of Blockchain Adoption in Finance
Adopting blockchain in the financial industry has huge potential, but it comes with several challenges:
1. Regulatory Uncertainty
One of the biggest issues is the lack of clear rules around blockchain and cryptocurrencies. Financial institutions are highly regulated, and the absence of consistent global guidelines makes it risky for them to dive into blockchain.
Therefore, governments need to create clearer, more consistent regulations. Initiatives like the EU’s MiCA are a step in the right direction, offering a legal framework to make adoption safer.
2. Data Privacy Concerns
Public blockchains make all transactions visible, and laws like GDPR require financial data to be erasable, which conflicts with blockchain’s permanent nature.
Permissioned blockchains, like Hyperledger, allow controlled access, balancing transparency and privacy. New tech, like zero-knowledge proof, can also help verify transactions without exposing personal information.
3. Integration Problems
Many financial institutions use old systems that are tough to integrate with blockchain. Plus, blockchain networks aren’t yet fast or scalable enough to handle the large number of transactions that big financial systems process. For instance, Ethereum can process 1 million transactions a day, but the demand is generally higher.
Projects like Ethereum’s Layer 2 solutions aim to improve speed and scalability. Banks and fintech companies also need to collaborate to make the transition smoother between traditional systems and blockchains.
4. Lack of Standards
Blockchain platforms often struggle to work together, creating compatibility issues. This discourages financial institutions from adopting the technology due to concerns about how well it will integrate with other blockchain systems in the future.
Future of Blockchain in Finance
Emerging blockchain trends have the potential to reshape how financial systems operate, challenging the traditional model and pushing towards a more decentralized and efficient finance industry.
1. Decentralized Finance (DeFi)
DeFi is a fast-growing trend that removes intermediaries like banks from financial services. It allows people to borrow, lend, trade, and earn interest without needing a central authority or bank. As it becomes more secure and user-friendly, DeFi might replace these banking functions.
Using DeFi platforms, people can manage these services directly through smart contracts. This shift could offer more control over personal finances, possibly making traditional banks obsolete.
2. Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs)
CBDCs are digital forms of national currencies issued by central banks, backed by the government for stability and regulation. Countries like China, with its digital yuan, and Sweden, with the E-krona, are already testing them to provide faster, more efficient transactions.
More nations could follow suit, fully digitizing their currencies. This can help central banks track financial flows and improve monetary control. CBDCs also promote financial inclusion, especially in developing countries where access to traditional banking may be limited.
3. Stablecoins
Stablecoins is a cryptocurrency that maintains a stable value by being linked to traditional assets like the US dollar or other commodities. Since their value stays steady, stablecoins could make it easier to use digital currencies in everyday life, bridging the gap between traditional finance and blockchain.
4. Web 3.0
Web 3.0 represents the next phase of the internet. It’s built on blockchain and decentralized applications (dApps). Unlike today’s internet, where big companies control most data, Web 3.0 aims to give users control over their own information. As a result, Web 3.0 could democratize the Internet and digital finance, making them more user-centered.
Blockchain Interoperability: Connecting Siloed Blockchain Networks
Another emerging trend is blockchain interoperability. This refers to the ability of different blockchain networks to communicate and share data with each other. Many blockchains operate independently, limiting their potential. Connecting these networks can significantly enhance collaboration, allowing assets and information to flow more easily between platforms.
Two blockchain projects that focus on connecting different platforms include:
- Polkadot: Uses a relay chain to link various independent blockchains called parachains, allowing them to share security and data. It also uses bridges to connect with external networks like Ethereum and Bitcoin.
- Cosmos: Uses a central system called the Cosmos Hub to manage the flow of information between blockchains. Blockchains (zones) can easily share data and assets through the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol, almost like how the internet connects different servers.
Real-World Case Studies: Blockchain in Action in Finance
1. Santander
Santander became one of the first global banks to issue a bond entirely on the blockchain. The bank issued a $20 million bond on the Ethereum blockchain in 2019. This automated the issuance and management of bonds, removing the need for intermediaries and paperwork.
2. Government of Estonia
Estonia is a pioneer in using blockchain to create a digital identity system for its citizens. The Estonian government has used blockchain to secure its citizens’ data and provide a range of digital services since 2012, including banking, voting, and medical records.
Today, 99% of the country’s transactions occur digitally. Furthermore, the digital authentication and signature system is estimated to save up to 2% of the country’s GDP each year.
( Also Read: Blockchain Technology: Challenges in the Finance Sector )
Final Thoughts
Blockchain is set to transform the modern financial world. It streamlines payment processes, reduces costs, and provides greater security compared to traditional systems. Although not without its challenges, the future looks bright with the development of CBDCs, Web 3.0, and interoperability platforms.
As blockchain continues to advance, it’s essential to stay in the loop on emerging blockchain trends and how they impact your own financial decisions. One thing’s for sure: blockchain has the potential to transform your cash management—whether you’re a business owner, an investor, or just managing your personal budget.
Frequently Asked Questions about Blockchain in Modern Finance
Q. How does blockchain improve financial security?
A. Blockchain improves security by decentralizing data, making it harder to hack. Once recorded, transactions can’t be altered, reducing fraud. Smart contracts also enforce agreements automatically, adding another layer of protection.
Q. Can blockchain reduce fraud in supply chain financing?
A. Yes, blockchain helps protect the supply chain by providing real-time, transparent records. These records help prevent fraud, such as double financing or invoice manipulation. An example is VeChain, which verifies transactions and tracks goods.
Q. How is blockchain used in sustainable finance?
A. While blockchain itself has a large carbon footprint, “green blockchain” systems are now in the works. Blockchain can be used to track environmental impacts and verify green projects. It ensures transparency in carbon credits. Platforms like SolarCoin also reward renewable energy production.



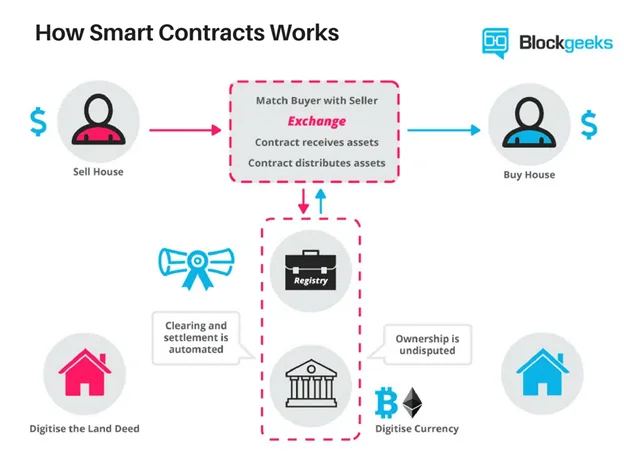
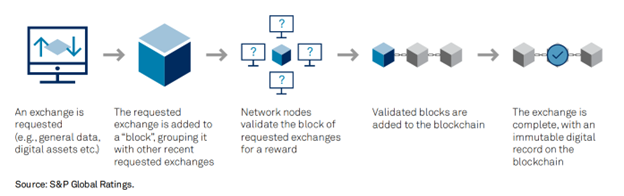
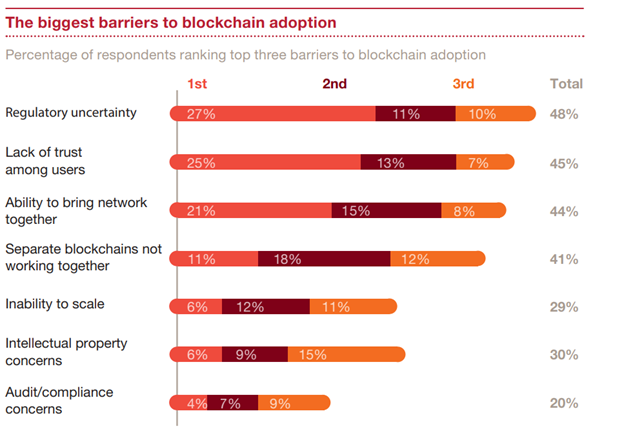 Image Source
Image Source






