Master data management or MDM is the enormous process used to centralize, organize, manage, categorize, localize, synchronize and enrich master data according to the business. Rules of the sales, marketing and operational strategies of your company is your master data management (MDM).
- In addition to that, 42% of enterprises around the world now see themselves as mobile-first.
- The Global MDM Enterprise Software market saw a projected growth at CAGR of 23.95% from 2013-2018.
- Frost & Sullivan also estimated the market for enterprise MDM to grow from $178.6 million in 2011 to $712.4 million by 2018*.
- What is Master Data?
- Types of Master Data Management
- Master data management definition
- MDM Roles
- MDM Implementation
- Why master data management?
- How does MDM Work?
- How does MDM help?
- Delayed MDM implementation vs Beginning MDM implementation
- How To achieve MDM Success
- MDM Architecture
- MDM gaining popularity
- Principles of MDM
- Features
- Master Data Management Security
- MDM Examples
- Disciplines of MDM
- Challenges
- Goals of MDM
- Master Data Management Capabilities
- FAQ’s
- Final Thoughts
What is Master Data?
Master Data refers to or describes the principal data that is of huge importance to operations in a specific business. It can be used to describe the tools, innovation, technology and processes that ensure that MDM is organized well in the enterprise.
What are the Different Types of Master Data and the Domains of Master Data?
Types of Master Data:
- The Reference Data
The reference data has been designed to represent the set of permissible values to be used by other (master or transaction) data fields.
- The Enterprise Master Data
This model is the single source of basic business data used across the entire enterprise, regardless of location.
- The Market Master Data
It symbolizes the single source of basic business data used across a marketplace, regardless of location. This is in contrast from enterprise master data in that it can be used by multiple enterprises within a value chain.
- The Unstructured Data
This is the Data found in white papers, email, magazine articles, product specifications, marketing collateral and PDF files.
- The Transactional Data
It is data concerning business events such as sales, deliveries, and invoices. They usually have historical significance or are needed for analysis by other systems.
- The Hierarchical Data
It stores the relationships between other data. It can be stored as part of an accounting system or separately as descriptions of real-world relationships.
Master Data Domains:
- The Customer Master Domain and Product Master Domain.
- Employee
- Asset
- Location and
- Financial entities
What is Master Data Management
Master Data Management is the standard procedure by which data is organized, centralized, localized, managed and synchronized to enrich your data according to your sales business rules. A business-oriented program, it is used to ensure that the organization’s master data is precise and accurate.
The Master Data Management initiative helps to remove unpredictability and upgrade overall business operations. The MDM concept encompasses the people, processes, and systems used to keep master data consistent.
Master Data Management Roles:
1) Data Governance
This is an interwoven cross-functional group of stakeholders that define the policies, standards, and processes for data management. The result of their efforts represents the requirements for the implementation of the MDM solution. Their function of governing also holds the data stewardship team accountable. The below defines the high-level roles within the governance team.
- The business Stakeholders: These are the various representatives for the interests of business functions across the organization, such as finance, marketing, HR, etc. Ideally, these individuals are in leadership or executive roles and they can break down barriers and provide credence to the outputs of the governance function.
- The business Analysts: Just like business stakeholders, business analysts are individual from across business functions, who do much of the legwork for the governance function, drafting the policies, standards, and processes for review and approval by the governance organizations.
- The Information Technology Stakeholders: They are Representatives from IT, typically a subset of those in the roles listed below, who help align the policies, standards and processes to the chosen Master Data Management (1) platform and make provision for a conduit for information back to the technical team.
2) Information Technology
They are leaders and technical resources in IT that install, configure, and maintain the data management solution. Some of their roles have dedicated resources, whereas others work on MDM on a part-time basis.
- The Solution Owner: The IT executive that owns the MDM solution from an IT perspective. This person manages the technical resources who are dedicated to MDM and often owns the relationship with the software vendor. Solution owner is typically an IT representative for governance.
- The Project Manager: Whose responsibility is to manage the day to day activities for the project team.
- The MDM Administrator: They are the experts at configuring the MDM platform itself, from data modeling, business rules, to the front-end user experience. At big organizations, these resources are often dedicated to MDM on a full-time basis.
- The Information Architect: Is a conduit between IT and the business to help design the data models and processes that will be implemented using the MDM platform.
3) Data Stewards
They are your business resources from Finance to Marketing and Sales to Operations. They are hands-on subject matter experts and are tasked with the actual management of data. They are informed and care about the data and its quality. They will be with the resources to fix, clean and manage data initially and on an ongoing basis.
Importance of Master Data Management
- MDM helps to ensure compliance with regulations and policies on data management.
- MDM helps to save time and reduce company’s operational costs.
- MDM ensures increase customer satisfaction by updating customer’s data and eliminating error
- MDM helps companies to increase in growth and scalability by increasing the amount of data they can handle.
- MDM assists companies to manage risk by eliminating errors and improving data quality.
How does Master Data Management work?
MDM works by transforming raw data into structured information product that can be used by other business processes. It manages and controls master data quality and usability of data by enhancing swift and precise access to information across the company’s platform.
Master Data Management functions as an organized method for solving data requirements of a business by using the reference data. An efficient Master Data Management system allows instant access to reference data by customers. In general, MDM helps by reducing operation costs, integrating systems and simplifying data structures.
How Does MDM Help You?
- MDM helps you to centralize your product, service and business activities on the actions that can improve the quality of sales.
- MDM helps the business to carry out and enhance customer service by creating a simple user interface experience.
- MDM helps to pinpoint costly and money draining activities that hinder business processes.
- MDM helps to centralize all business data by deleting duplicates in other departments, updating and storing information at a precise location.
- Overall, MDM helps to enhance business operations and reduce risk.
How to implement Master Data Management.
The following are the steps to follow to implement master data management: –
- You should tie Master Data Management to business, process improvement initiative.
- After which you should Identify all master data assets related to that process improvement initiative.
- Don’t forget to evaluate and profile the current status of your initiative’s data quality.
- Then, identify all necessary data integration for systems of record and those subscribing systems that will contribute to, or ultimately benefit from MDM’s good and consistent data.
- Which would lead to you determining the most efficacious MDM implementation style to support the relationships for data exchange between the MDM Hub and all participating enterprise systems.
- Also, select a flexible and versatile Master Data Management solution that can govern and link any sharable enterprise data and connect any business domain, including reference data, metadata, and hierarchies.
Differences between implementing MDM at the beginning versus fixing the issues of existing data and systems:
| Delayed MDM Implementation | MDM Implementation from the Beginning |
|---|---|
| It has duplicate processes in silos and costly developments | There will be efficient and faster development with lower cost |
| It has data quality issues everywhere with no easy way to track down | There will be Fewer data quality issues that are faster to fix |
| There is also low customer satisfaction | The customer satisfaction will be very high |
| The data asset potentials are not fully realized | There is opportunity to generate more revenue |
| It is very difficult to migrate to new data platform | It is much easier to migrate to new data platform when needed. |
How To Achieve Master Data Management Success.
-
Set up a Data authority accepted by the Entire Organization
By establishing and revising data governance policies and procedures, it helps to prioritize and make decisions proficiently. This resolves conflicts and improves management success by describing how data assets should be used and accessed under a well secured and regulated MDM database.
-
Apply MDM to New Data Additions/Applications
The use of MDM in an organization requires consistency and commitment for it to be successful. Data policies and regulations should be implemented throughout all data platforms. Disregarding MDM at the onset of every new project in the business will lead to increased effort and costs overall.
The most efficient way is to begin every new project with MDM which helps to increase experience and specialization in the organization. The best way to start with MDM is to apply it for going forward for new projects, which will test it out first and enable the organization to build up expertise and experience. This ensures enforced by Quality Assurance (QA) testing and User Acceptance Testing (UAT).
-
Selecting the Right MDM Software
Any model MDM software should have the following features:
– Referencing and access to master data resources within a company.
– Facilitate information and data regulations to classify and easily modify the definitions.
– Proficient at analyzing and reviewing the data, to adequately organize and enforce data regulations in the business.
These characteristics make the MDM tool perfect for data integration within an organization and participate in more critical roles.
- Influence the MDM Capability to Manage Existing and Legacy Systems: the use of MDM on existing data assets may require a lot of effort, time and money. In order for MDM to be successful it requires careful planning and strategy to apply and integrate MDM to the business platform. Application of MDM to new master data, applications and processes can improve and establish new data platforms along with the MDM.
Also read: Effective Benefits of Master Data Management for Businesses
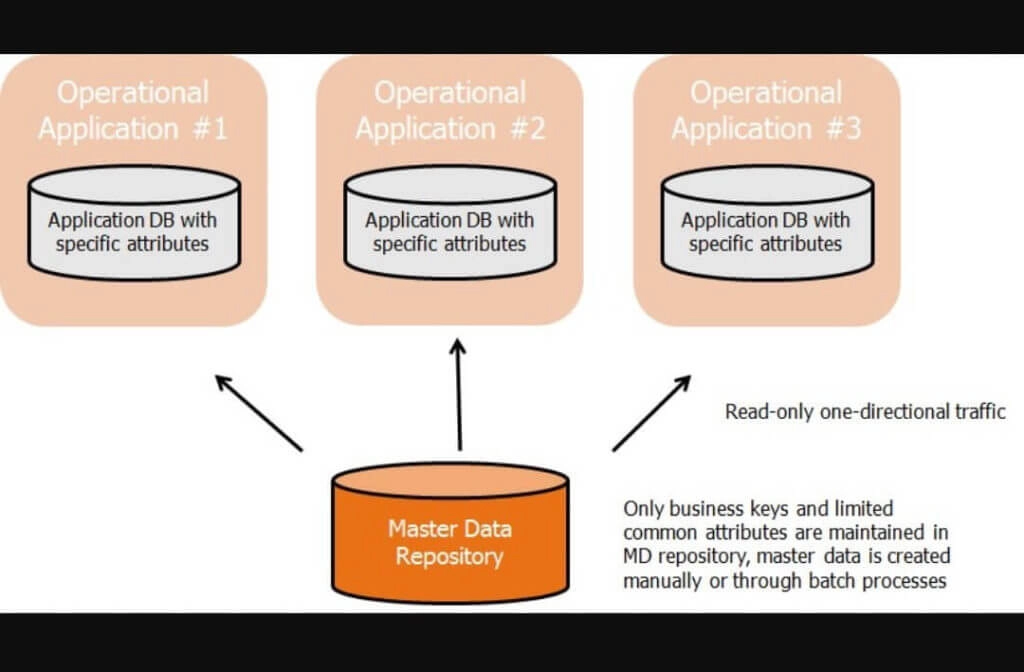
Master Data Management Architecture
-
Registry Architecture
This architecture provides a read-only view to master data for downstream systems that need to read but not modify master data. This implementation architecture is useful to remove duplicates and provide (in many cases federated) a consistent access path to master data.
The data in the MDM System is often only a thin slice of all the master data attributes which are required to enforce uniqueness and cross-reference information to the application system that holds the complete master data record. In this scenario, all attributes of the master data attributes remain with low quality without harmonization in the application systems except for the attributes persisted in the MDM System.
Thus, the master data is neither consistent nor complete regarding all attributes in the MDM System. The advantage of this architecture is that it is usually quick to deploy and with lower cost compared to the other architectures. Also, there is less intrusion into the application systems providing read-only views to all master data records in the IT landscape.
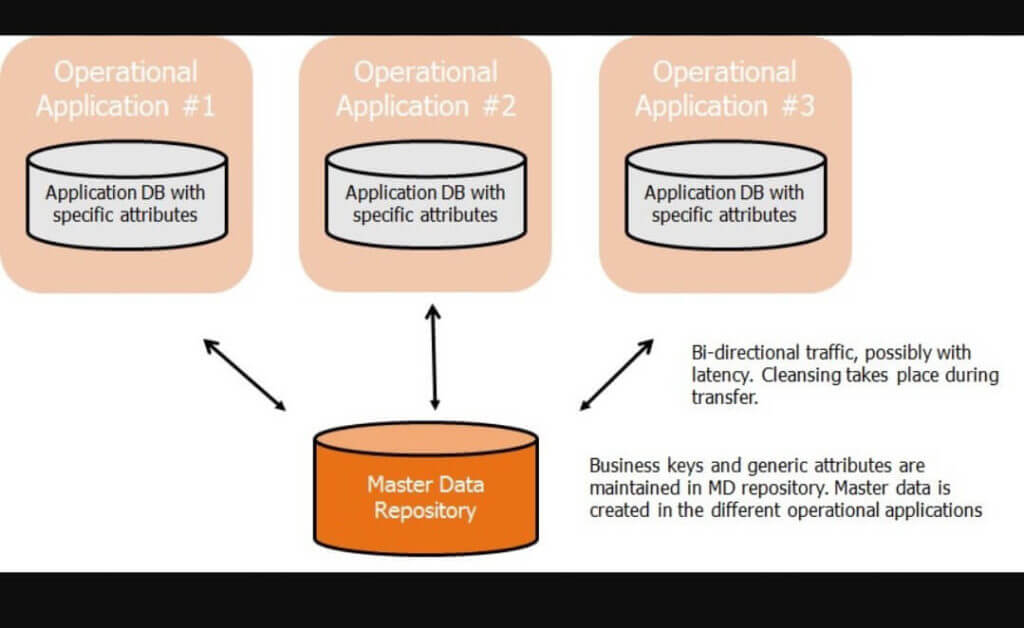
-
Hybrid Architecture
This architecture fully materializes all master data attributes in the MDM System. Authoring of Master Data can happen in the MDM System as well as in the application systems. From a completeness perspective, all attributes are there. However, from a consistency perspective, only convergent consistency is given. The reason for this is that there is a delay in the synchronization of updates to master data in the application systems distributed to the MDM System. This means consistency is pending. The smaller the window of propagation, the more this implementation architecture moves towards absolute consistency.
The cost of deploying this architecture is higher because all attributes of the master data model need to be harmonized and cleansed before loaded into the MDM System which makes the master data integration phase more costly. Also, the synchronization between the MDM Systems and application systems changing master data is not free.
However, there are multiple benefits of this approach that are not possible with the Registry Architecture implementation:
- The master data quality is significantly improved.
- The access is usually quicker because there is no need for federation anymore.
- Workflows for collaborative authoring of master data can be deployed much easier.
- Reporting on master data is easier as now all master data attributes are centralized.
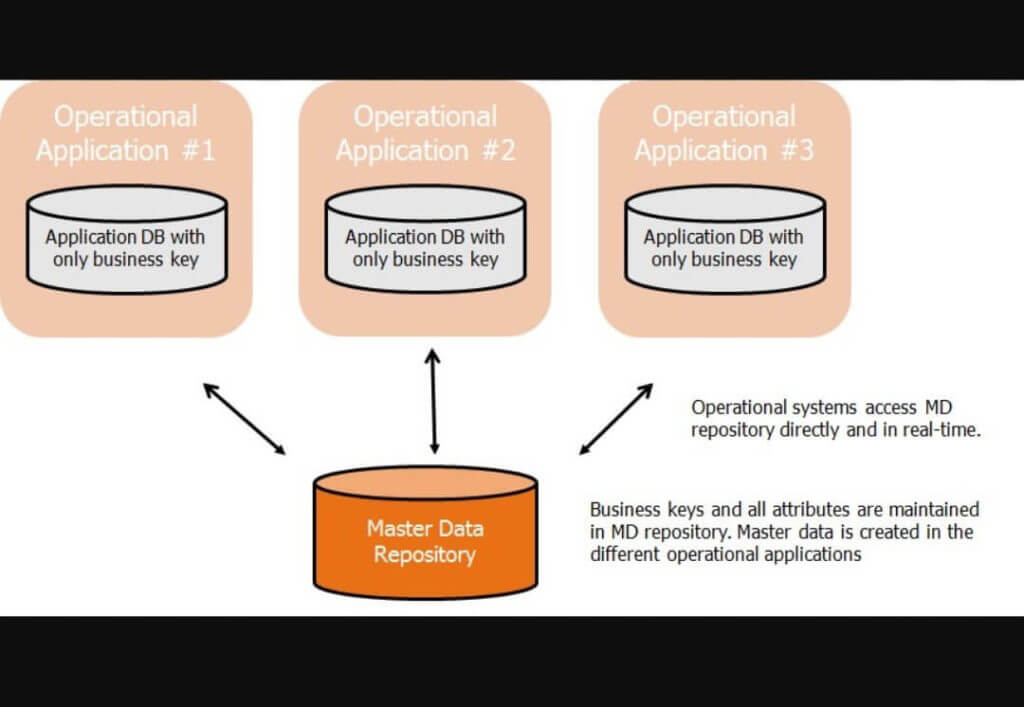
-
Repository Architecture
With this architecture, master data is consistent, accurate and complete at all times. The key difference to the Hybrid Architecture is that both read and write operations on Master Data are now done through the MDM System. Achieving this means that all applications -with the need to change master data- invoke the MDM services offered by the MDM System to do so.
As a result, absolute consistency on master data is achieved because the propagation of changed master data causing delay no longer exists. Deploying an MDM solution with this architecture might require deep intrusion into the application systems, intercepting business transactions in such a way that they interact with the MDM System for master data changes or the deployment of global transaction mechanism such as a two-phase commit infrastructure.
Why is MDM becoming so popular?
Well, the main reason MDM is becoming very popular especially among large business organizations is because of its efficiency, productivity and flexibility.
Principles of Master Data Management.
-
Data Integrity
The output of any system is only as good as its input. If you put in the right thing, you get the right thing. It is this accuracy that is referred to as data integrity. As you have seen, and going by the very name of the topic, data is at the center of MDM. And if the data which is relied upon by all the departments is inaccurate, then everyone suffers. As mentioned at the beginning, data is needed to make the right decisions. This is mainly facilitated by report generation.
The system will generate reports based on the data it has been fed with. The system may, for example, indicate that there are 480 pieces of the product that you sell. You may then decide to reduce production so as to avoid overproduction. This is a business decision that has obvious implications.
On the ground, you may have 400 pieces and not 480. If you sell 370 pieces then get an order for 100 more, you may think that you have the stock for it. And this is where the problem will come in. You may either think that stock has been lost or find out that the wrong data was entered. Your order may be delayed as you restart production. The customer may also become inconvenienced because of delayed delivery.
This is a clear demonstration of the importance of accuracy in data entry. In the same way, MDM is affected by such mistakes. This is why data integrity is a must. When building the repository, the data must be checked for accuracy and consistency. Where variations are found, the correct version should be identified and used.
-
Data Governance
Closely related to data integrity is data governance. Data governance is simply the act of ensuring continued data integrity. Data governance is concerned with the integrity of all the data that is entered into the system well after the MDM solution is in place. Data governance is usually implemented as a program. That, however, does not make it an external part of the process.
Data governance is basically the maintenance of the system. It comes with rules determining the format in which the data is to be in, the process to be followed and in some cases, even the frequency of data entry. These are rules which are set to uniquely fit individual needs. If your company is constantly adding new types of products, then you can remove the restrictions accordingly. But certain types of data, for example under the finance department, should ideally have restrictions.
-
Change Management and Accountability.
The data in the system is never completely unchanging.
There will be instances when changes need to be made. The customer address scenario above is a good example. But that doesn’t mean that data changes can be done by just anyone at any time. Accountability must be enforced to protect the integrity of the system. Ideally, there should be one person in every department who is mandated with the role of making changes. This helps in ensuring that the number of people accessing the core of the system is reduced. For example, you might have 5 sales representatives who go to the field. If one gets an update about a customer’s information, he should pass it on to another staff who has the system rights to make the changes. In the right implementation, each one of these employees could have a view of the customer data. But their limited rights should not enable them to make changes.
-
Auditability
Audits should not only happen in the finance department, but also on the MDM system. Auditability, in this case, refers mainly to the proof of the processes followed while making changes into the system.
If for example, a new company is to be created in the system, there should be an approval process followed. If a customer is to be created, there should be an approval granted for the same. This will provide the records to show what exactly happens behind the scenes.
For auditability to work, data governance must be in place. With the rules set for new data and data changes, the integrity of the whole system can be maintained. This then guarantees the correctness of the reports which are generated by the system.
Master Data Management Features
-
Matching and Linking
Matching and linking features help to efficiently manage large volumes of company data. The MDM reduces the risk of having duplicates of company data thereby reducing confusion and maintaining the reliability and preciseness of corporate information.
-
Applying Specific Business Rules
This feature places the MDM software in the position to help assist the business by setting defined rules for the organization. This feature is business-specific and can be used to meet an individual’s business expectations. This allows an ease of use that reduces risk, set rules for data integrity, company policies, and so much more.
-
Manage Location-Based Data
This important feature helps to maintain and manage customer data across borders, i.e. in other countries. It restricts the access to data in some country specific regions hereby improving customer data security.
-
Enhanced Data Security
The security of data is very important to an organization. The MDM tool offers the capacity to secure data by creating regulations and policies. Part of these features includes the use of user passwords to keep vital private information safe and away from third-party intrusion. This ultimately assists in protecting sensitive customer and staff data by using encrypted data to generate security-based rules.
-
Implementing Data Enrichment
Adding value to data through correct analysis and improvement naturally makes it more valuable and essential. It makes the information an asset and more versatile for several applications. To do this the following steps are crucial:
- Efficiently manage product and catalog data.
- Guarantee high degree of data quality
- Update your digital asset supervision
- Endeavour to meet up with the data requirements of retailers.
Master Data Management Security
MDM must be well implemented with security as it plays an important role in its consideration. The MDM’s focuses in an organizations data integrity to ensure smooth business operations. For proper coordination of security measures when implementing MDMs, it is advised to add a data governance program which regulates how data is produced, maintained, stored and destroyed and also on how changes are approved and audited.
Master Data Management Examples
- Reference data: these may be known as acceptable values in other data such as standard currency codes
- Customer data: these are the most common type of master data and must be handled properly because it is essential to a large number of processes.
- Product data: this is a product list that contains product information and specification.
- Employee data: this represents all data on an employee.
- Transactions: this represents data on business dealings such as purchases.
- Tickets: these many be used to follow up issues, problems and customer complaints resulting from a transaction.
- Analytical data: this data is used to support important decision making in an organization.
The Six Disciplines of MDM Include –
- Governance
- Measurement
- Organization
- Policy
- Process
- Technology.
Master Data Management Issues/Challenges.
-
Tooling
In the world of Master Data Management tooling is getting more crucial every day but how do you select the right one? What is the purpose and goal of this toolset? Think clear and think about the future needs of your company.
-
The Why Question
The importance of “why” is often misunderstood. It is critical to get everyone on board and provide them with knowledge of the importance of Master Data Management. Empower the business and the people to get them fully understand the benefits.
-
Governance
Master Data Management can be complex just by being master data. Just look at modeling and standards within your own master data. Clear policy and business rules around Master Data take out complexity. Introduce governance to get a clear overview of responsibilities.
-
Go back to start
Where do you start with the management of master data? Create a starting point for is the first important thing to do. Did you make the right preparations? Is everything in place to take on with “professional” Master Data Management? If not, do not hesitate to go back to start and draw the new sketch
-
Sponsorship
Sponsorship from preferably c-level or senior management is a crucial element for success. The decision maker must stand behind the goal and knows the importance of the project.
-
Model Definitions
A Master Data model is usually not clear or not yet in place. So, defining the model with different layers of first-tier, second-tier master data or meta-data is crucial to make integration of master data simpler and more understandable.
-
Talent and Knowledge
Master Data Management is not just a project. Master Data Management should be considered as the backbone of organizations. Combining knowledge from experienced people and young talent helps to deliver a structure and the result you are aiming for. Get a “balanced” team in place who have the capabilities to do the job.
Goals of Master Data Management
- The primary goal of Master Data Management (MDM) is to promote a shared foundation of common data definitions within your organization, to reduce data inconsistency within your organization, and to improve overall return on your IT investment.
- A reasonable level of standardization across the MDM processes exists.
- MDM processes are handled consistently across the organization.
- The MDM lifecycle is effectively controlled, while allowing for speed and agility.
- An organization is in place to make key, critical business decisions regarding the data. This organization is recognized, respected and utilized
Master Data Management Capabilities
- Transparency
- Business Intelligence
- Compliance
- Time-to-Value
- Automation
- Data Deluge and Complexity: it can process tons of complex data records efficiently.
- High Quality Data
- Data Lineage
- Cost effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions about Master Data Management
Q. Master Data Management Use Cases
A. Following are the cases
- Data Management for Data Warehousing: This ensures data for use are processed in real time analytical processing so that users can decrease the data capture time until it is needed for analysis.
- Data Management for Analytics: this particularly intended to support analytical processing and also the use of machine learning and data science programming languages.
- Data Management for Governance: Data governance is majorly made up of a set of frameworks developed specifically to guarantee reliable and excellent data. Implementing a govern
- Data Management for Compliance: the use of Data management software is very vital for keeping data regulations and compliance. With the high attention given to the current state of data privacy and protection, this makes this a vital use case for master data management.
Q. Difference between Data Governance v Master Data Management
A.
| Data Governance | Master Data Management |
|---|---|
| Data Governance is an important component in any corporate data management strategy | Master Data Management is the most important data that needs to be managed in an organization. |
| Data governance is the initiative a company takes to create and enforce a set of rules and policies regarding its data. | Master Data Management is the initiative a company takes to organize, manage, assess, prioritize and secure their data. |
Q. Who Should Be Involved In MDM Programs?
A. These are involved
- Program manager
- Project manager
- System administrator
- Developer
- Business analyst
- Data architect
- End users
- Governance council
Q. Where can I learn more about MDM?
A. Learn more about MDM using online digital learning platforms such as VISO MDM.
Final Thoughts
Management of master data is an essential part of any business process, it is necessary for every business establishment to be able to fully recognize and utilize its data potential and prospective income to achieve success.
The application of a sustainable master data management system is a big issue since data quality measurement and monitoring has to be done on a continuous basis. Therefore, preventative measures need to be taken to guarantee a smooth process flow.
In order to have an efficient MDM process, the company needs to be committed to making it a permanent component of the data strategy, it should entail reliable governance and support from the top management and other business departments.
The difficulty of fixing existing data and system issues should not hinder the application of MDM. The core goals of MDM concept should be clear based on the business benefit, it is advisable to apply MDM to all new data sources and applications. This will gradually lay the groundwork for its use on existing data and systems.